The undercounter freezer is an efficient and indispensable solution in the food industry, especially in restaurants, hotels, and industrial kitchens. […]
Read More

- News
HACCP System: What is HACCP? 7 Standards and Implementation of HACCP
- November 9, 2023
HACCP, short for “Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points,” is a specialized food safety management system widely applied in the food industry, playing a crucial role in ensuring food safety for consumers. HACCP certification has become a significant factor for businesses in the food industry to demonstrate their commitment to providing safe and high-quality products.
In this article, we will provide you with an overview of HACCP system, including its definition, objectives, standards, and the process of implementing HACCP. We will delve into the essential aspects of this system, helping you understand how it operates and why it plays a vital role in safeguarding consumer health and instilling confidence in the food they consume daily.
In this article
What is HACCP system?
Definition
HACCP, an abbreviation for “Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points,” is renowned as a powerful tool in ensuring food safety. Beyond being a mere end-product control process, HACCP system is a complex system that assists food businesses in systematically and scientifically identifying and managing food-related risks.
In today’s world, food safety and hygiene are not just legal responsibilities but also ethical commitments for food businesses. HACCP system helps them identify potential hazards from biological, chemical, and physical factors in the food production process and integrates them into a rigorous control system. HACCP doesn’t just inspect the final product; it aims to prevent risks from the beginning. Rather than reacting after an issue occurs, this system ensures that harmful agents have no opportunity to cause food poisoning.
HACCP system doesn’t exist in isolation; it can be integrated with other management systems, such as ISO 22000 Food Safety Management, creating a robust network for food safety and consumer health.
The HACCP system consists of seven basic steps but can be customized based on the specific nature of each industry, menu, customer requirements, and specific production tools and processes. This flexibility makes HACCP suitable for various specific situations.
Next, let’s explore the 7 HACCP standards for restaurants with Saigon Horeca!
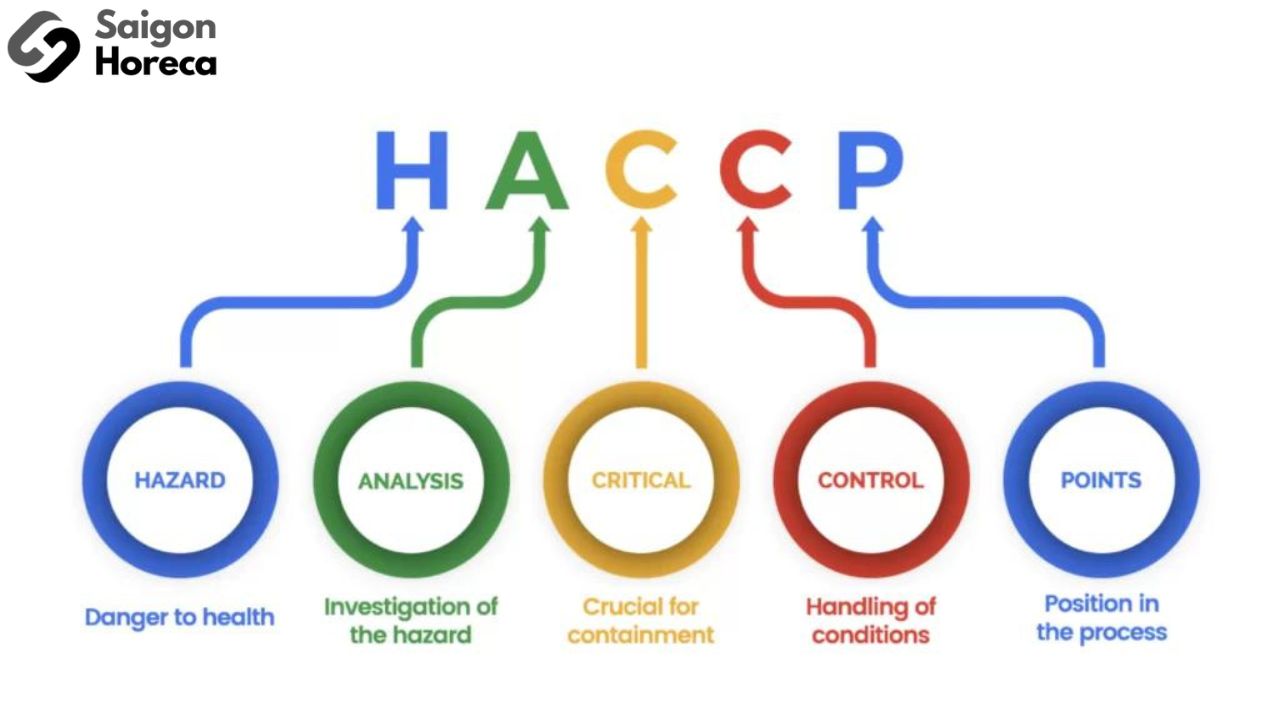

7 HACCP Standards for Restaurants
Crucial Foundations in the HACCP System
When establishing an HACCP system process for a restaurant, analyzing hazards is the crucial first step. By creating a measure to control hazards, we can assess potential risks in the food preparation process, especially when dealing with Time/Temperature Control for Safety (TCS) foods*.
Processes to be examined in food preparation include:
- Preparing non-heat-treated foods, such as salads, fruits, and raw meats.
- Preparing cooked foods, such as grilled meats or ready-to-eat foods.
- Red peppers, soups, and sauces prepared in advance, refrigerated, and reheated before serving.
- Foods like potato salads and mixed salads prepared in advance and stored.
During the evaluation, you need to identify hazards related to chemical, biological, and physical factors that may occur. A practical example is grilled chicken being prepared, cooked, and sold on the same day. Potential hazards often include biological agents, such as bacteria, especially when chicken is not thoroughly cooked. This leads us to concerns about food safety and the need to control the handling of this food item with caution.
- TCS: Time/Temperature Control for Safety (TCS) foods refer to foods that need to be controlled for time and temperature to ensure food safety.


Identifying Critical Control Points (CCP) – Another Pillar of HACCP Compliance for Restaurants
When adhering to HACCP Standards in a restaurant environment, identifying how to deal with potential hazards is a crucial and indispensable step. This requires pinpointing specific processes and decision points – known as Critical Control Points (CCP) – to control and minimize risks related to food safety. CCP is a crucial decision point where control must be implemented to ensure food safety.
These critical control points often include significant stages in the food preparation and serving process, such as:
- Receiving Food from Suppliers: The process of receiving food from suppliers requires inspection to ensure the quality and safety of raw materials.
- Pre-food Preparation Storage: Storing food before preparation must ensure that temperature and storage conditions are safe.
- Food Handling and Pre-processing: The process of handling and pre-processing food must be executed with care to prevent cross-contamination.
- Cold and Hot Holding of Food: Maintaining a safe temperature for food during storage and transportation is crucial.
- Cooking and Reheating Food: The cooking and reheating process must adhere to temperature and time standards to ensure safety.
- Transfer of Pre-processed Food to Different Areas: During the transfer of food from the kitchen to the serving area, control is necessary to ensure safety and hygiene.
- Hot and Cold Holding of Food During Service: Maintaining a safe temperature for food throughout the serving process is a crucial decision.
Specific Example: When cooking chicken breasts, this could be considered a Critical Control Point (CCP) because the cooking process helps eliminate or reduce bacteria to a level safe for consumers. This is a point where risk control is extremely important to ensure food safety.






Critical Control Points (CCP) – A Crucial Pillar in Restaurant HACCP Compliance
Building an effective HACCP system in a restaurant environment involves identifying Critical Control Points (CCP), which play a crucial role. CCPs are points in the food processing process where control must be implemented to ensure food safety. They help prevent, eliminate, or reduce potential hazards.
Examples of CCPs include:
- Receiving Food from Suppliers: Checking the quality and safety of ingredients right from when they enter the restaurant.
- Pre-food Preparation Storage: Ensuring safe temperature and storage conditions to prevent the growth of harmful bacteria.
- Food Handling and Pre-processing: Adhering to food hygiene rules to prevent cross-contamination.
- Cooking and Reheating Food: This requires adherence to temperature and cooking time rules to ensure food is cooked to a safe level.
- Transfer of Pre-processed Food to Different Areas: This needs control to ensure safety and hygiene during the transportation of food.
- Hot and Cold Holding of Food During Service: Maintaining a safe temperature for food throughout the serving process to ensure consumer safety.
A specific example is cooking chicken breasts, which is a crucial CCP because it eliminates or reduces the risk of harmful bacteria. Control at these CCPs is a decisive factor in ensuring food safety in a restaurant.
Monitoring and Adjusting Control Limits
An equally crucial part of the HACCP system is monitoring and adjusting the set control limits. This requires active involvement from those responsible for overseeing the food processing process. Designate a monitor and establish the frequency of checking these limits. This includes:
- Adjusting control measures if any deviations or trends in deviations are detected.
- Promptly identifying any deviations and taking corrective action immediately.
- Recording information about the HACCP process for use when necessary.
Specific example: To illustrate, consider monitoring the temperature of a cooking chicken breast using a cleaned and sanitized temperature probe. Insert the temperature probe into the thickest part of the chicken breast. Each piece of chicken must be cooked for 15 seconds with the internal temperature reaching a minimum of 74 degrees Celsius.
Corrective Action When Limits Do Not Meet Food Safety Standards
If a limit does not meet standards, it is considered a deviation. In such cases, staff should know how to rectify the error. This involves:
- Clearly identifying the cause of the deviation.
- Implementing corrective procedures if possible.
- Documenting the procedures for correcting this deviation.
Specific example: An example is when, after checking the temperature, a chicken breast does not reach the required temperature even though it was cooked for the specified time. In this case, the process of cooking additional chicken breasts is carried out to ensure the internal temperature reaches 74 degrees Celsius within 15 seconds. This additional cooking time is recorded.


Establishing an Effective HACCP Documentation Storage Procedure
Regularly reviewing and updating HACCP standards is important to ensure the effectiveness of the process. Use all records, documents, and monitoring charts to get an overview of the process and ensure its effectiveness. This raises an important question: Has the HACCP plan been successful in preventing, minimizing, or eliminating hazards in food?
Specific example: In this step, a manager can review the temperature chart after each shift, checking whether the temperature limit for chicken breasts has been reached each time this dish is cooked. By monitoring temperature charts, the manager can identify the action trends of the staff and adjust the entire process accordingly.
Accurate record-keeping is a crucial factor in making the operation against food hazards more organized and effective. Developing a reliable HACCP documentation storage procedure is the final step in implementing the HACCP process. This involves establishing a storage procedure, assigning a supervisor, and setting clear regulations on how information will be stored initially, as well as the update process.
Some important documents to be stored include:
- A list of the members of the HACCP implementation team and the tasks of each person.
- A preliminary description of the foods involved in the HACCP process.
- A flow chart of the food processing process with annotations of the control points.
- Details about the hazards at the control points and corresponding preventive measures.
- Control limits.
- Monitoring systems, such as temperature logs.
- Records of how to correct deviations.
- HACCP record-keeping procedures.
- Information about suppliers, including commercial invoices for transportation and other specific information.
Specific example: Temperature monitoring charts, records of how to correct deviations, and commercial invoices for the chicken processing process are stored for 6 months. Other specific information about grills and the warranty policy of the grills is stored for about a year. If any issues arise, this information can be used to support and verify the HACCP process. This ensures transparency and the ability to efficiently check the process.


The procedure for obtaining a food safety certificate that meets HACCP standards
Saigon Horeca will guide you through the important steps to obtain a food safety certificate that meets HACCP standards. The HACCP certificate is not only an important factor to ensure the safety of the food you produce or supply, but also a commitment to quality and compliance with safety procedures. Let’s start with the first step in this process: contacting and exchanging information with the certification body.
Step 1: Contact and Exchange Information with the Food Safety Department
Before starting the process of obtaining an HACCP food safety certificate, the contact and exchange of information between the business and the Food Safety Department is an important first step. In this meeting, key information to be coordinated includes:
- Specific steps in the HACCP certification process.
- Basic requirements and standards applied.
- Costs and fees related to the certification process.
- Schedule and HACCP implementation plan.
Step 2: Prepare the Preliminary HACCP Assessment File
The business will submit the HACCP registration file to the certification body. This file includes the following documents and papers:
- HACCP certification registration form.
- HACCP implementation plan.
- Documents and records related to the application of HACCP standards.
Experts from the Food Safety Department will conduct a practical assessment of the HACCP standard compliance. This aims to identify weaknesses in the documentation and the application of the HACCP system in the business. At the same time, this process also helps the business establish Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulations.
Step 3: Sign the HACCP Certification Contract
After the preliminary assessment of the file, the business and the Food Safety Department will sign a contract to issue the HACCP certificate. This officially starts the inspection and evaluation process.
Step 4: Provide HACCP Files and Documents
The business will provide the certification body with files and documents related to HACCP.
Step 5: Formal Evaluation of HACCP Files
All documents and materials related to HACCP, including the HACCP handbook, will be formally evaluated for the compliance of the HACCP system with relevant regulations and standards.
After reviewing and formally evaluating the documents, the assessment report will be prepared, and a copy will be sent to the business.
After receiving this report, the business will review and make corrections if necessary.
Step 6: Plan the Inspection
The business and the evaluation team will plan the inspection, on-site assessment. This plan must be agreed upon by both parties.
Step 7: Inspection and On-Site Assessment
The evaluation team will conduct the inspection and on-site assessment, evaluating the compliance of the submitted documents with reality. At the same time, the evaluation team will recommend corrections to any non-compliance.
Step 8: Receive the HACCP Certificate
If all the documents are compliant with reality and any non-compliance points have been corrected, the business will be issued an HACCP certificate valid for 3 years.
Step 9: Maintain Certification and Apply for Recertification
During the validity period of the HACCP certificate, the business must regularly monitor to ensure compliance with HACCP standards. If any non-compliance issues are detected and the business does not rectify them promptly, the HACCP certification may be revoked.


Key Terms in Standards
In the process of implementing and adhering to the HACCP procedure, understanding key terms in the industry is crucial. Let’s delve into some important terms that you need to grasp:
- GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices): A system guiding the proper production and processing of food. GMP applies to food manufacturing and processing facilities, encompassing the management of every aspect of the production process to ensure product quality and food safety.
- Biological Contamination: Refers to disease-causing agents in food, including bacteria, viruses, pollen, and other living organisms with the potential to cause illness.
- Chemical Contamination: Relates to substances that are not normally present in food, such as acrylamide, benzene, dioxin, melamine, which can be harmful if consumed.
- Corrective Action: The process that must be undertaken when a critical control point fails to meet or exceeds safety limits. The goal is to eliminate or minimize the identified hazard to a safe level.
- Food Hazards: These are agents that pose a danger to food, including biological, chemical, or physical agents that have the potential to cause harm or illness if not well-controlled.
- Monitoring: Using observation and measurement systems to track critical control points. This ensures that limits are maintained and well-controlled. Information collected from the monitoring process can be recorded for storage and reference purposes.
- Physical Contamination: Refers to the loss or introduction of foreign objects into food, such as bone fragments, rubber bands, hair, and other objects that can cause injury or illness.
- TCS (Time/Temperature Control for Safety) Foods: These are types of food that require careful control of time and temperature to ensure safety for consumers.
Monday - Friday
from 8h00 to 18h00
Số 40 Đường số 6, KDC Melosa Khang Điền, Phú Hữu, HCM.
Contact anytime
Related Posts
Structure and Operation of the Multi-functional Baking Oven: Professional Baking Equipment
Sweet cakes, bread, sponge cakes, and various other types of pastries are indispensable delights in the daily lives of people. […]
Read More




